Cybersecurity Terms Decoded: A Beginner's Guide
In today's digital world, cybersecurity is more important than ever. Whether you're browsing the web, managing online accounts, or working remotely, understanding key cybersecurity terms can help you stay safe. This guide breaks down essential cybersecurity concepts in simple terms.
1. Malware#
Malware (short for malicious software) is any program designed to harm, exploit, or damage devices and networks.
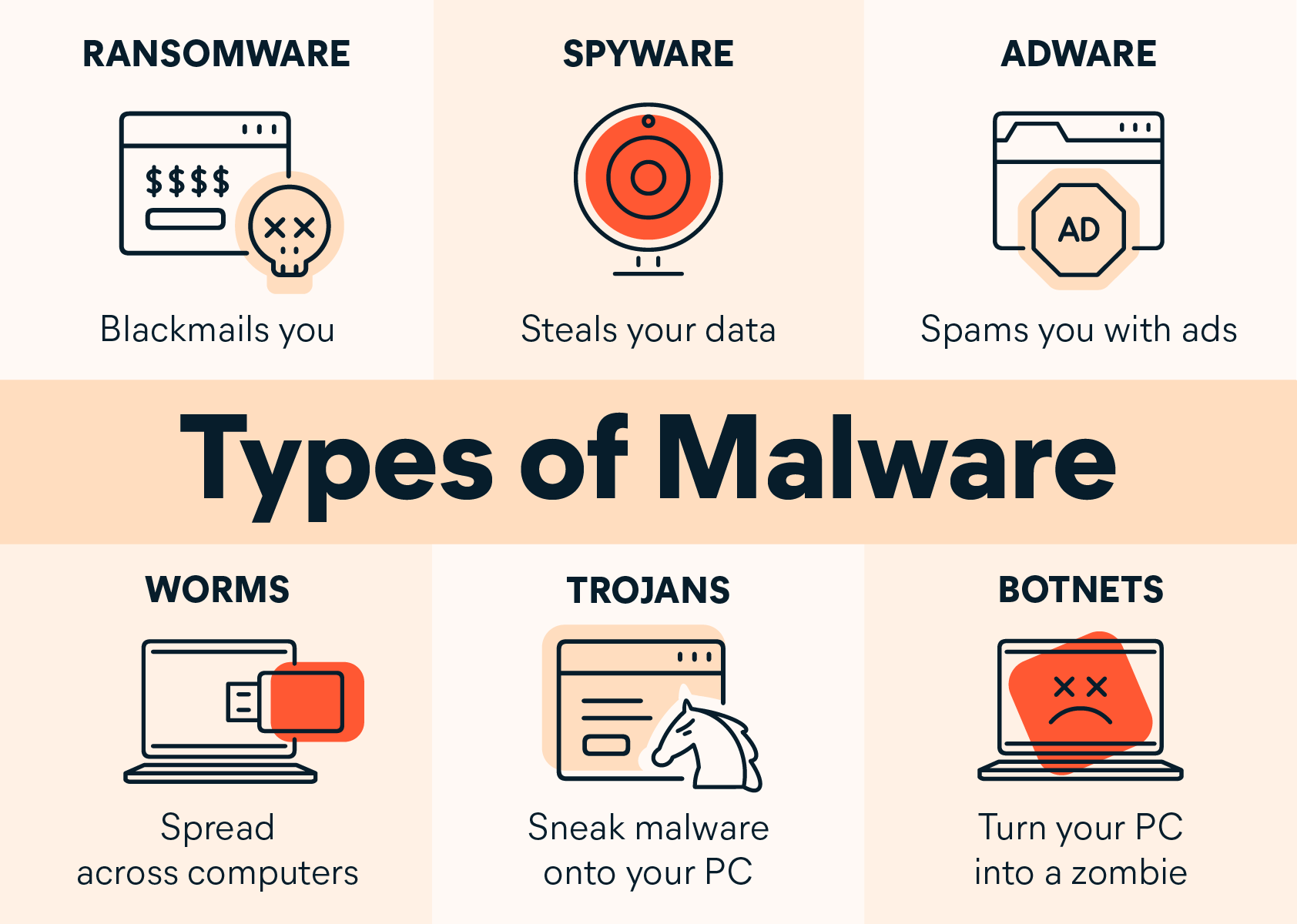
Common Types of Malware#
- Viruses: Attach themselves to files and spread when executed.
- Trojans: Disguised as useful programs but perform harmful actions.
- Worms: Self-replicate and spread across networks without user action.
- Spyware: Secretly tracks user activity and sends data to attackers.
- Adware: Displays intrusive ads and can track browsing behavior.
💡 Prevention Tip: Keep your OS and software updated and use a reliable antivirus program.
2. Phishing#
Phishing is a cyberattack where hackers trick users into revealing sensitive information by pretending to be a trustworthy source.
How Phishing Works#
- You receive an email that looks like it's from your bank.
- It contains an urgent message: "Your account has been locked. Click here to verify."
- Clicking the link takes you to a fake website that looks like your bank's login page.
- If you enter your credentials, hackers steal your login details.
Example: Fake Phishing Email#
From: [email protected]
Subject: Urgent! Account Verification Needed
Dear Customer,
We noticed suspicious activity on your account.
Please confirm your details immediately to avoid account suspension.
[Verify Now] (malicious link)
Best,
Your Bank's Security Team
💡 How to Stay Safe:
- Never click suspicious links in emails.
- Check the sender's email address carefully.
- Use 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication) for extra security.
3. Ransomware#
Ransomware is a type of malware that locks or encrypts your files and demands payment (a ransom) to restore access.
How Ransomware Works#
- You download an infected attachment or click a malicious link.
- Your files become encrypted and inaccessible.
- A message appears: "Pay $500 in Bitcoin to recover your files."
- If you don't pay, you lose access permanently.
💡 How to Protect Yourself:
- Keep regular backups of your data.
- Don't download attachments from unknown sources.
- Use security tools that detect ransomware threats.
4. Zero-Day Attack#
A Zero-Day Attack occurs when hackers exploit a software vulnerability before the developer releases a fix. Since the issue is unknown to the software vendor, there's zero time to fix it before exploitation.
Why "Zero-Day"?#
The term "zero-day" signifies that developers have zero days to patch the vulnerability before hackers start using it.
How It Works#
- A hidden security flaw exists in the software.
- Hackers discover and exploit the flaw before the vendor is aware.
- The attack spreads before a security patch is released.
- Developers rush to fix the issue, but unpatched systems remain vulnerable.
💡 Did you know: The Stuxnet worm, which targeted Iran's nuclear program, was one of the most sophisticated zero-day exploits ever discovered.
Example: Exploiting an Unpatched Software Bug#
# Example of a zero-day exploit concept (not actual attack code)
def vulnerable_function(input_data):
if input_data == "unexpected_value":
return "System crashed!" # Attackers exploit this to inject malicious code.
💡 How to Stay Safe:
- Enable automatic updates for your software and OS.
- Avoid downloading software from untrusted sources.
- Use Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) to monitor unusual behavior.
5. Firewall#
A firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules.
How Firewalls Work#
- Packet Filtering: Inspects data packets and allows or blocks them based on security rules.
- Stateful Inspection: Tracks active connections and blocks unauthorized access.
- Proxy Firewall: Intermediary between users and the internet, filtering malicious traffic.
Example: A Simple Firewall Rule in Python#
import socket
def block_ip(ip_address):
blocked_ips = ["192.168.1.10", "203.0.113.42"]
if ip_address in blocked_ips:
print("Access Denied!")
else:
print("Access Granted!")
block_ip("192.168.1.10")
💡 How to Stay Secure:
- Keep your firewall enabled, especially when using public Wi-Fi.
- Use hardware firewalls for an extra layer of protection.
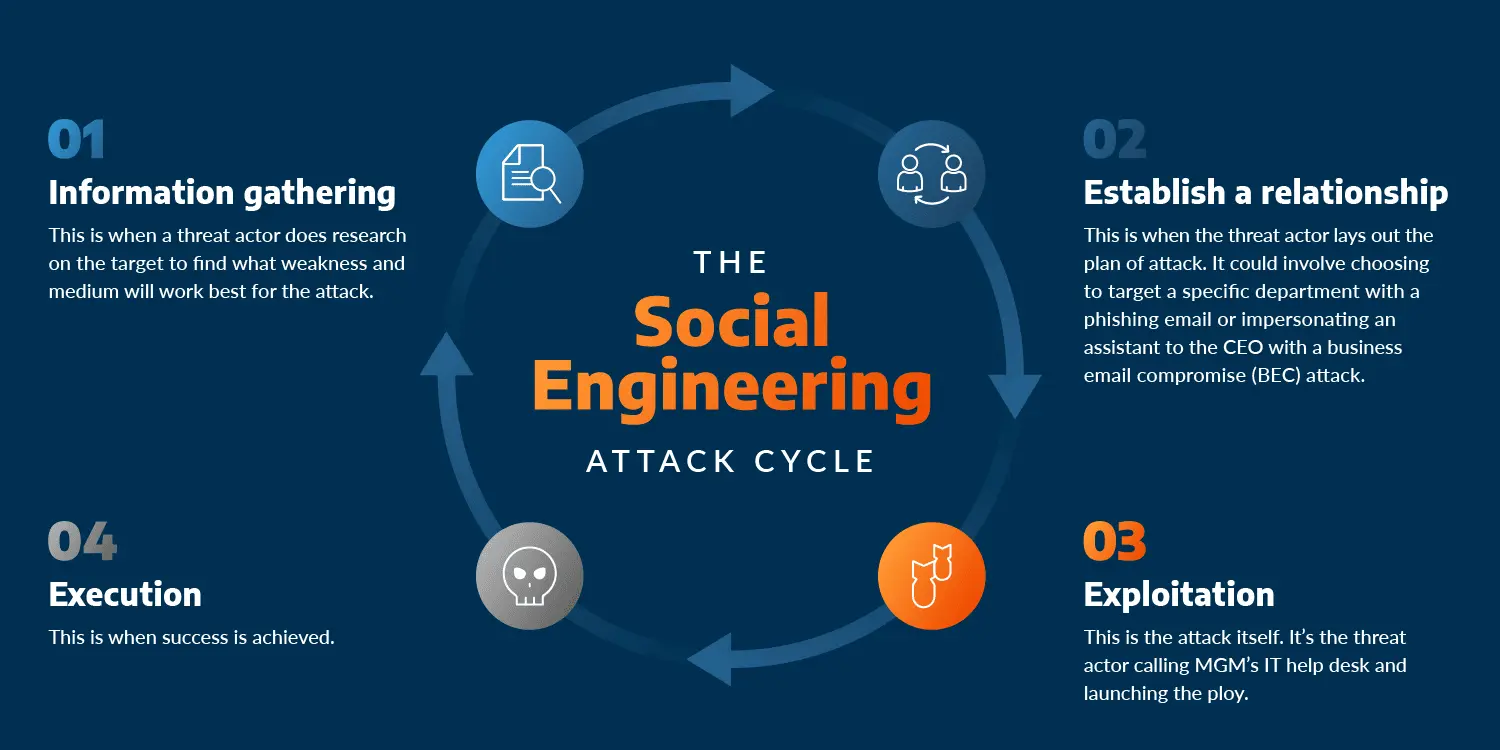
6. Social Engineering#
Social engineering is when hackers use psychological tricks to manipulate people into revealing confidential information.
Common Techniques#
- Pretexting: Pretending to be a trusted figure (e.g., IT support) to get information.
- Baiting: Leaving infected USB drives in public places to trick users into plugging them in.
- Impersonation: Using fake social media profiles to steal personal data.
💡 How to Protect Yourself:
- Never share sensitive information over phone calls or emails without verifying the source.
- Be cautious of unsolicited help requests.
7. VPN (Virtual Private Network)#
A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making your online activities private and secure.
Why Use a VPN?#
- Prevents hacking on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Hides your IP address to prevent tracking.
- Bypasses geo-restrictions to access content unavailable in your region.

💡 Best Practices: Always use a VPN from a trusted provider with a no-log policy.
8. DDoS Attack#
A DDoS (Distributed Denial-of-Service) attack overwhelms a website or server by flooding it with excessive traffic, causing it to crash.
How DDoS Attacks Work#
- Hackers infect thousands of devices with malware, forming a botnet.
- The botnet sends massive amounts of requests to a website.
- The website crashes due to overload.
Example: A Basic DDoS Simulation in Python#
import requests
url = "http://target-website.com"
while True:
requests.get(url) # Continuously sending requests to overload the server
💡 How to Defend Against DDoS:
- Use cloud-based security services to absorb large traffic spikes.
- Enable rate-limiting on web servers.
Final Thoughts#
Understanding these cybersecurity concepts is crucial for staying safe online. Cyber threats evolve daily, so staying informed and using security best practices can help protect your data.
Next Steps: Enable 2FA, use strong passwords, and stay cautious online.
Stay tuned for more tech content and tutorials. Hit me up on my socials and let me know what you think, I'm always up for a good tech convo.
stay updated.
It's free! Get notified instantly whenever a new post drops. Stay updated, stay ahead.