Introduction to AI Agents: How to Build a Simple AI Agent Using Python and GPT-4
What are AI Agents?#
AI agents are programs or systems that act autonomously to achieve specific goals by perceiving their environment and making decisions. Think of them as digital assistants—sometimes as simple as a thermostat adjusting the temperature, other times as complex as virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa answering your questions.
According to resources like What are AI Agents?, they come in two main flavors:
- Rule-based agents that follow predefined instructions
- Machine learning-based agents that adapt from data over time.
How They Work?#
- Perception: They gather data from their surroundings, like a user's voice command, sensor readings, or online weather stats.
- Reasoning: They process that data using logic, rules, or algorithms—sometimes even learning from past experiences—to figure out what to do next.
- Action: They execute a task, whether it's adjusting a setting, answering a question, or suggesting an outfit.
These agents power everything from chatbots handling customer support to Netflix's recommendation engine, silently improving everyday digital interactions.
Types of AI Agents#
AI agents come in various flavors, each suited to different tasks:
- Simple Reflex Agents: These follow basic "if-then" rules. For example, if the temperature drops below 20°C, suggest a jacket.
- Model-Based Reflex Agents: These keep a mental model of the world. Imagine an agent that remembers yesterday's weather to guess if you'll need an umbrella today.
- Goal-Based Agents: These aim for specific outcomes, like ensuring you're comfortable in any weather, even if it means juggling multiple factors like rain and wind.
- Utility-Based Agents: These optimize for the best result, maybe suggesting the coziest outfit based on your preferences.
- Learning Agents: The smartest of the bunch, these improve over time. Picture an agent that learns you hate coats and swaps them for hoodies, as noted in AI Agents: 5 Key Types Explained With Examples.
Real-World Examples#
AI agents are everywhere, often hiding in plain sight:
- Chatbots: Customer service bots on websites use NLP to answer queries, a staple example from 36 Real-World Examples of AI Agents.
- Recommendation Systems: Netflix suggests shows based on your viewing history—pure agent magic.
- Robotic Agents: A Roomba vacuum navigates your floor, dodging obstacles with sensors and actuators.
- Virtual Assistants: Siri or Google Assistant handle tasks like scheduling or weather checks, blending perception and action seamlessly.
Why Use AI Agents for Everyday Tasks?#
Tired of repetitive tasks? AI agents can lift that burden. Automating tasks like checking the weather or scheduling meetings saves time, reduces errors, and enhances convenience. For instance, instead of flipping through apps to see if it will rain, an AI agent can fetch the forecast and suggest a raincoat—before you even ask.
The benefits don't stop there. These agents can integrate with smart devices—imagine one tweaking your thermostat based on the day's weather. It's about working smarter, not harder, and that's why we're building one today.
Create a Simple AI Agent: A Weather-Based Clothing Suggester#
Design the Agent#
Before we code, let's outline what our agent should do:
- Understand You: Recognize user phrases like "What to wear?" or "What should I wear today?"
- Get Your Location: Prompt for city and country code (e.g., "London,uk").
- Fetch Weather Data: Use OpenWeatherMap API to get current weather conditions.
- Make Suggestions: Apply practical clothing rules based on the data.
Clothing suggestion logic:
- Below 10°C: "Heavy coat, gloves, and boots."
- 10–20°C: "Light jacket or sweater."
- Above 20°C: "T-shirt and shorts."
- If it's raining: Add "Bring a raincoat or umbrella."
These rules are inspired by the Simple Guide on What to Wear in 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, and 80 Degree Weather.
Code It in Python#
We will use Python for its simplicity and the requests library to interact with external APIs.
Setup Steps:
- Install dependencies:
pip install requests openai - Get a free API key from OpenWeatherMap.
- Replace
"YOUR_OPENWEATHERMAP_KEY"and"YOUR_OPENAI_KEY"in the script. - Run the code.
import requests
from openai import OpenAI
import traceback
def get_weather(location, api_key):
url = f"http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q={location}&appid={api_key}&units=metric"
try:
response = requests.get(url)
response.raise_for_status()
data = response.json()
if 'main' in data and 'weather' in data:
temperature = data['main']['temp']
condition = data['weather'][0]['main']
return temperature, condition
else:
raise ValueError(f"Incomplete weather data: {data}")
except requests.RequestException as e:
print(f"[ERROR] Weather API request failed: {e}")
traceback.print_exc()
raise
except Exception as e:
print(f"[ERROR] Weather data parsing failed: {e}")
traceback.print_exc()
raise
def ask_chatgpt(temperature, condition, location, openai_api_key):
client = OpenAI(api_key=openai_api_key)
prompt = f"The weather in {location} is {temperature:.1f}°C with {condition}. Based on this, what should I wear today? Keep it short and helpful."
try:
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-turbo",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
max_tokens=100,
temperature=0.7,
)
suggestion = response.choices[0].message.content
return suggestion.strip()
except Exception as e:
print(f"[ERROR] ChatGPT API call failed: {e}")
traceback.print_exc()
raise
def main():
print("Hi! I'm your weather wardrobe assistant. What can I help you with?")
user_input = input().lower()
if "what to wear" in user_input or "what should i wear" in user_input:
print("Great! Where are you? Enter your city and country code (e.g., 'Tokyo,jp'): ")
location = input()
weather_api_key = "YOUR_OPENWEATHERMAP_KEY"
openai_api_key = "YOUR_OPENAI_KEY"
try:
temperature, condition = get_weather(location, weather_api_key)
print(f"[INFO] Weather fetched successfully: {temperature:.1f}°C, {condition}")
suggestion = ask_chatgpt(temperature, condition, location, openai_api_key)
print(f"For {location}, it's {temperature:.1f}°C with {condition}. {suggestion}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"[ERROR] Something went wrong: {e}")
else:
print("Sorry, I only help with clothing suggestions. Ask me what to wear!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Real-World Examples#
Example 1:
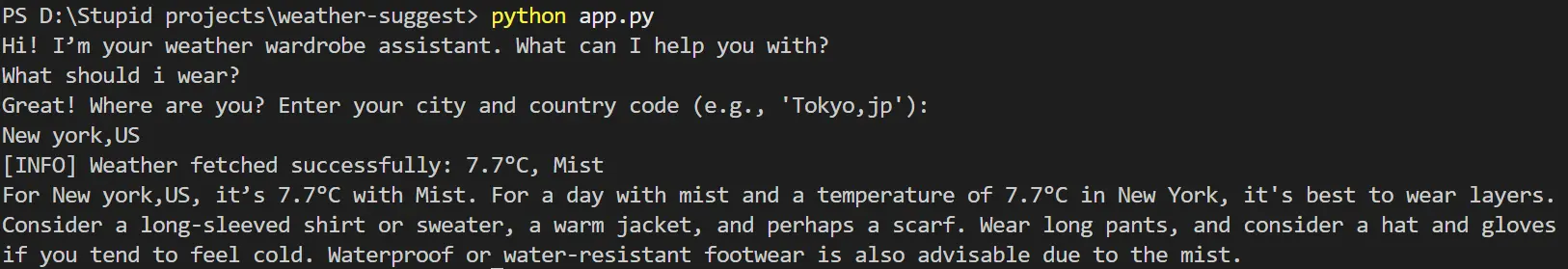
Input: "What should I wear today?" → Location: "New York,us"
Weather: 7.7°C, Mist
Output: "For New york,US, it's 7.7°C with Mist. For a day with mist and a temperature of 7.7°C in New York, it's best to wear layers. Consider a long-sleeved shirt or sweater, a warm jacket, and perhaps a scarf. Wear long pants, and consider a hat and gloves if you tend to feel cold. Waterproof or water-resistant footwear is also advisable due to the mist."
Example 2:
Input: "What to wear?" → Location: "Hyderabad,In"
Weather: 25.7°C, Clear
Output: "For hyderabad,in, it's 25.7°C with Clear. For a clear day in Hyderabad with a temperature of 25.7°C, it's best to wear light, breathable clothing. Opt for a T-shirt or a light top, comfortable pants or shorts, and a pair of sunglasses. You might want to carry a light jacket or a shawl for the evening in case it gets cooler."
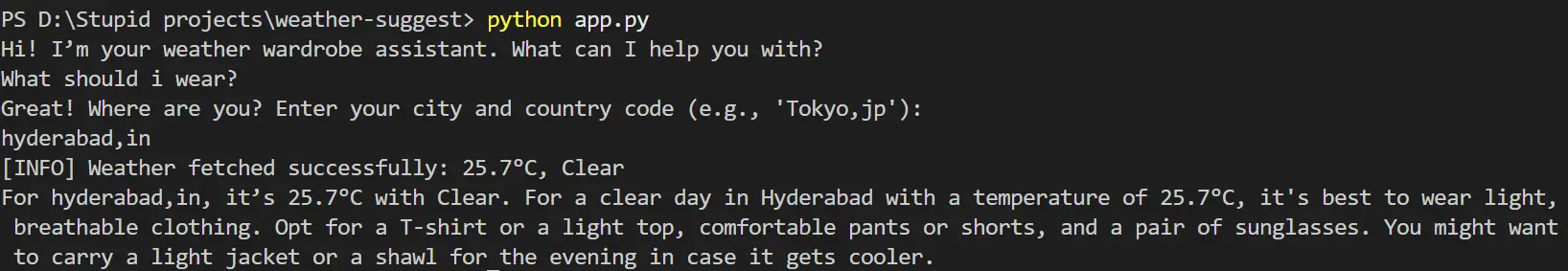
These examples show how the agent adapts to different climates and conditions, making it a handy tool worldwide.
Test and Tweak#
Test with:
- Cold days (e.g., "Moscow,ru" in winter)
- Hot, rainy days (e.g., "Bangkok,th")
- Invalid locations (e.g., "Narnia") to verify error handling.
Want to level up? Add:
- Wind-based checks ("Wear a scarf if windy")
- UV alerts ("Bring sunglasses on sunny days")
- Personalization ("Skip jackets, I prefer hoodies")
Taking It Further#
Here's how to take this agent to the next level:
- Smarter Chat: Integrate NLP libraries like
nltkto handle diverse user queries. - Preference Learning: Let your agent learn your clothing preferences over time.
- Integrations: Connect it to smart speakers, messaging apps, or home automation systems.
Would you like me to also generate a downloadable "starter project repo" with README for this?
Why This Matters#
Building this agent isn't just about skipping a weather check—it's about unlocking AI's potential. It's proof that with a few lines of code, you can automate the mundane and focus on what matters. Plus, it's fun! You've now got a tool that blends tech and practicality, backed by solid sources like Weather API - OpenWeatherMap.
So, fire up your editor, grab that API key, and let your AI agent dress you for success. What task will you automate next?
Stay tuned for more tech content and tutorials. Hit me up on my socials and let me know what you think, I'm always up for a good tech convo.
stay updated.
It's free! Get notified instantly whenever a new post drops. Stay updated, stay ahead.